Key Considerations for Selecting Flexible Fill-Finish Manufacturing Technologies
There is increasing demand for advanced manufacturing technologies for fill-finish operations of parenteral drug products. To meet manufacturing requirements for multiple container and component types, flexible fill-finish equipment is at the forefront of most pharmaceutical, biotech, and CDMOs’ fill-finish strategy. Flexible fill-finish technology is suitable for variable batch sizes allowing for scaling from clinical to commercial in multiple drug delivery presentations. With the ability to launch in vial configurations, prefilled syringes, or other combination products including devices, flexible fillers are beneficial to drug developers who are looking for lifecycle management of their drug products.
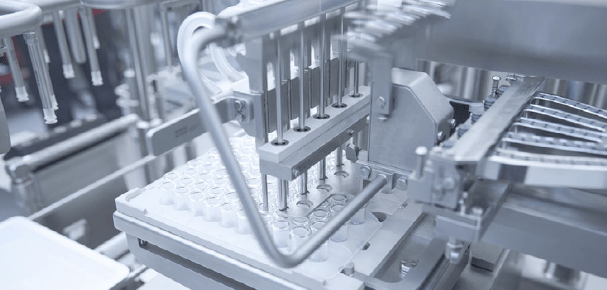
Filling and plunger placement of nested pre-fillable syringes as they reside in their nest. Image courtesy of Bausch+Ströbel. Used with permission.
However, not all fill-finish original equipment manufacturers (OEM) are the same. Building or expanding manufacturing capabilities requires multiple factors that need to be evaluated: maximization of floorspace, reducing risk of cross-contamination, manufacturing flexibility, varying throughput, tech transfer, and various primary packaging formats. Further, to ensure that an investment in flexible fill-finish equipment meets long-term needs, there are some critical aspects that need to be considered upfront.
Some key considerations that need to be taken into account when selecting flexible fillers include:
- Whether to choose a Restricted-Access Barrier System (RABS) or Isolator.
- Line speed
- Component types
- Format parts
- Packaging removal
- Container transport mechanism
- Closure defect prevention
- Pump mechanism
- Wetted path
- Vacuum filling
- Number of dosing stations
- Dosing accuracy verification
- Inert-gas purge capability
- Piston placement capability
- Number of stopper/piston placement stations
- Electrostatic reduction
- Particulate control and monitoring
- Material out-flow
- In-line inspection and rejection
- Automation and data management.
The recently revised EU GMP Annex 1, Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products1 guideline advises that the introduction of materials into the clean room or filler is one of the single greatest sources of contamination. Therefore, careful selection of packaging configurations (i.e., nested trays, ported bags, steribags, or bulk components) based on the designated manufacturing facility and filler design is an important decision and must be considered as a design input to support Quality Risk Management (QRM) and Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) implementation. These aspects will determine of level of protection of drug product from contamination, cost of equipment as well as added operational costs, lifecycle management of drug into different packaging formats , and overall safety and efficiency of the manufacturing process.
When considering these critical details, choosing the right flexible fill-finish OEM may be a daunting task. West recognizes the importance of proactively working with flexible fill-finish OEMs during development of components to ensure compatibility of their equipment for proper handling, filling, and processing for intended use with our primary packaging systems. For customers with existing equipment, rather than requiring the fabrication of a new filling line or line addition, some parameterization, process tuning, or format part change-overs may be required so that primary packaging can be processed as intended. This can improve manufacturing readiness and help get customer closer to commercialization.
As you look to work with a CMO or build internally for your flexible fill-finish operations, West can help identify container closure solutions that will work with your manufacturing processes. To learn more about these fill-finish features, read our whitepaper here. For more information, visit our fill-finish page.
References
- The Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the European Union Volume 4 EU Guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use, Annex 1, Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products. https://www.pda.org/topic-areas/eu-annex-1-revision




