Most frequently asked questions on the revised EU GMP Annex 1: Volume 3
In August 2022 the European Union revised its guidelines for sterile medicinal products for human and veterinary use. These guidelines came into effect on August 25, 2023. West has compiled the most frequently asked questions about Annex 1 and how it affects sterile drug manufacturers, which will be published across a multi-part series.

1. What countries are affected by EU GMP Annex 1?
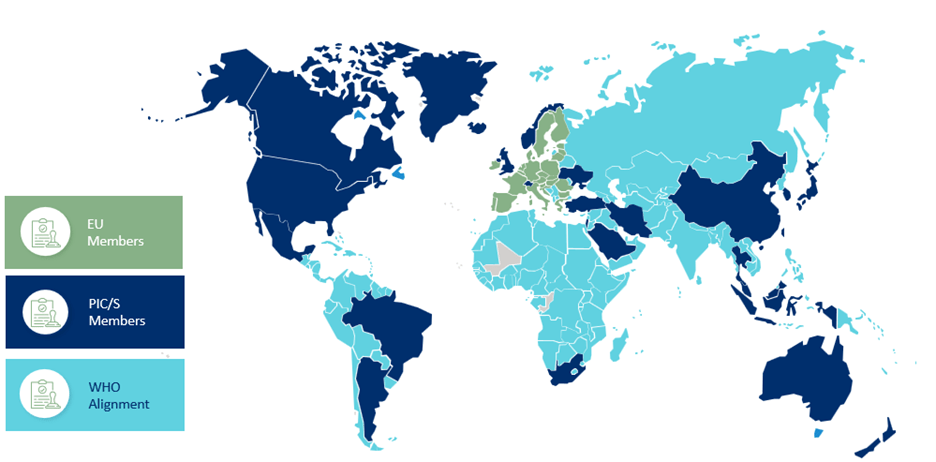
The 2023 Annex 1 revision covers manufacturing, packaging and distribution and applies to all sterile medicinal products manufactured in the European Union and the UK. It also applies to other parts of the world that are intending to export into the EU and UK, and, as the revision is a product of the collaboration between the EC, EMA, PIC/S, and WHO Alignment, all organizations in those countries must abide by the regulations, as seen in the map below.
2. What are the major changes in the 2023 revision?
The most notable changes are:
- Greater importance of a contamination control strategy (CCS) for the end-to-end manufacturing process
- Revised and expanded guidance on the use of restricted access barrier systems (RABS) and isolators for aseptic production
- Enhanced sterility testing and validation processes
- Stricter requirements for environmental monitoring, in particular Grade A zone continuous monitoring
- Cleanroom design must highlight airflows and clear delineation between critical and less critical zones
- More detailed guidance on water systems, filtration and media fills
3. What is a CCS?
A CCS is a comprehensive plan that covers all aspects of sterile manufacturing to minimize the risk of contamination. The strategy includes cleanroom design, air handling systems, personnel practices, equipment and process validation, cleaning and disinfection procedures, and environmental monitoring. The latest Annex 1 revision requires manufacturers to implement and maintain a CCS to ensure sterility and product quality.
4. Does it matter where packaging component sterilization occurs?
This could be in-house at the pharmaceutical manufacturer, at a contract manufacturer or at the component manufacturer’s site. There is no mandate in the revision as to where this must happen, but the site largely influences how the process is controlled and validated. The primary concern is not the physical location of sterilization, but the focus should be on the robustness of the sterilization process, how it is integrated into the overall manufacturing process, and how it meets the required standards.West offers ready to use and ready to sterilize components. Outsourcing to component suppliers can be a valid resource as many companies have steps in place to ensure sterility and assist in compliance.
5. If packaging components are sourced presterilized, what documentation should the drug manufacturer expect from the supplier?
A component supplier plays a critical role in helping the drug manufacturer comply with the Annex 1 revision and, as such, should ensure the quality, sterility and compliance of materials or components they supply. Whilst documentation provision can be varied, critical documentation includes:
- A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) or Certificate of Conformance (CoC)
- Traceability records and validation reports• Change control and deviation management
- Environmental monitoring and cleanroom data
- Sterility validation and bioburden data
6. How do RABS & isolators help with EU GMP Annex 1 compliance?
Whilst not obligatory, these technologies are specifically recommended for drug manufacturers to comply with the Annex 1 revision as they are critical parameters influencing compliance. Both systems can enhance contamination control by reducing the risk of microbial and particulate contamination. These technologies minimize human interventions in sterile manufacturing areas, as personnel are the greatest source of contamination.
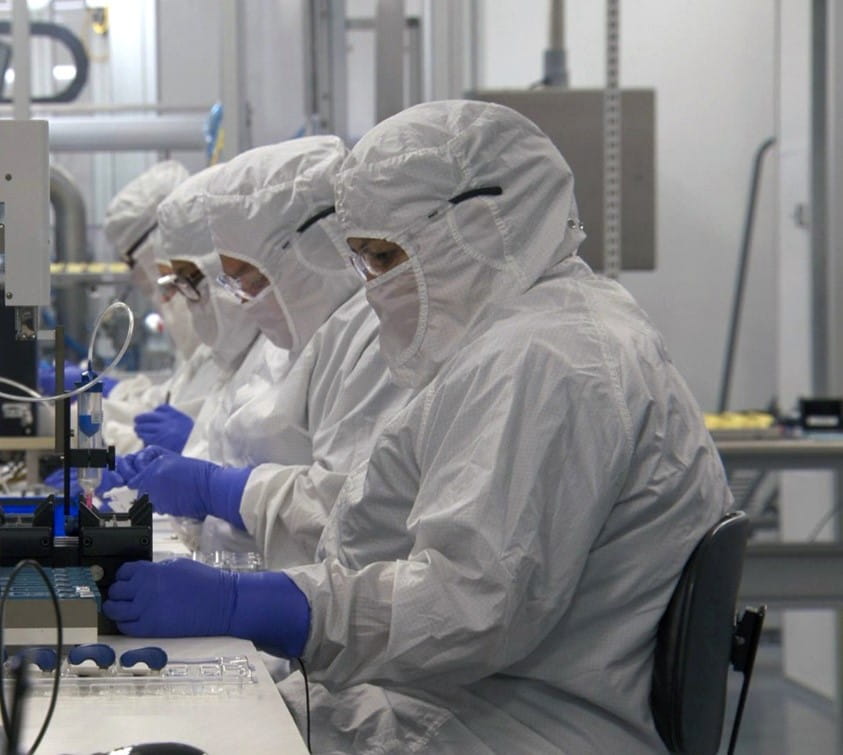
7. As personnel and human interventions pose risk to sterile manufacturing, what impact has this had on the guidelines for gowning and training of personnel?
There is clear recognition within the revision that personnel add risk to contamination control as significant emphasis has been placed on training and gowning where:
- Personnel must receive robust and regular training on cleanroom behavior, aseptic techniques and impact to contamination control
- In-depth gowning procedures are well communicated, documented and reinforced to ensure the correct clothing (hoods, gloves, masks, gowns etc.,) is worn for the different cleanroom grades
Subsequent gowning qualification competency must be demonstrated with regular requalification. In terms of extractables information we have available for our modern formulations, theoretical documents that are not based on experimental extraction studies and provide general chemical compound groups or names based upon the manufacturer's knowledge of what is used in the manufacture of the components and what reactions they might yield.
Want to learn more? Click to access blog 1 and blog 2 in the Annex 1 FAQ series.
To speak with an Annex 1 expert, click here
Learn more about meeting EU GMP Annex 1 requirements.




