Flip-Off® Seal Cap Removal Testing
The traditional way to package injectable drugs is to place them in a stoppered vial. The stopper is typically held in place with an aluminum ferrule that is called a seal. The vial seal is crimped onto the vial and not only serves to keep the stopper secured to the vial and the vial contents sterilei but also protects the injection site on the stopper and provides a means of demonstrating lack of tampering.
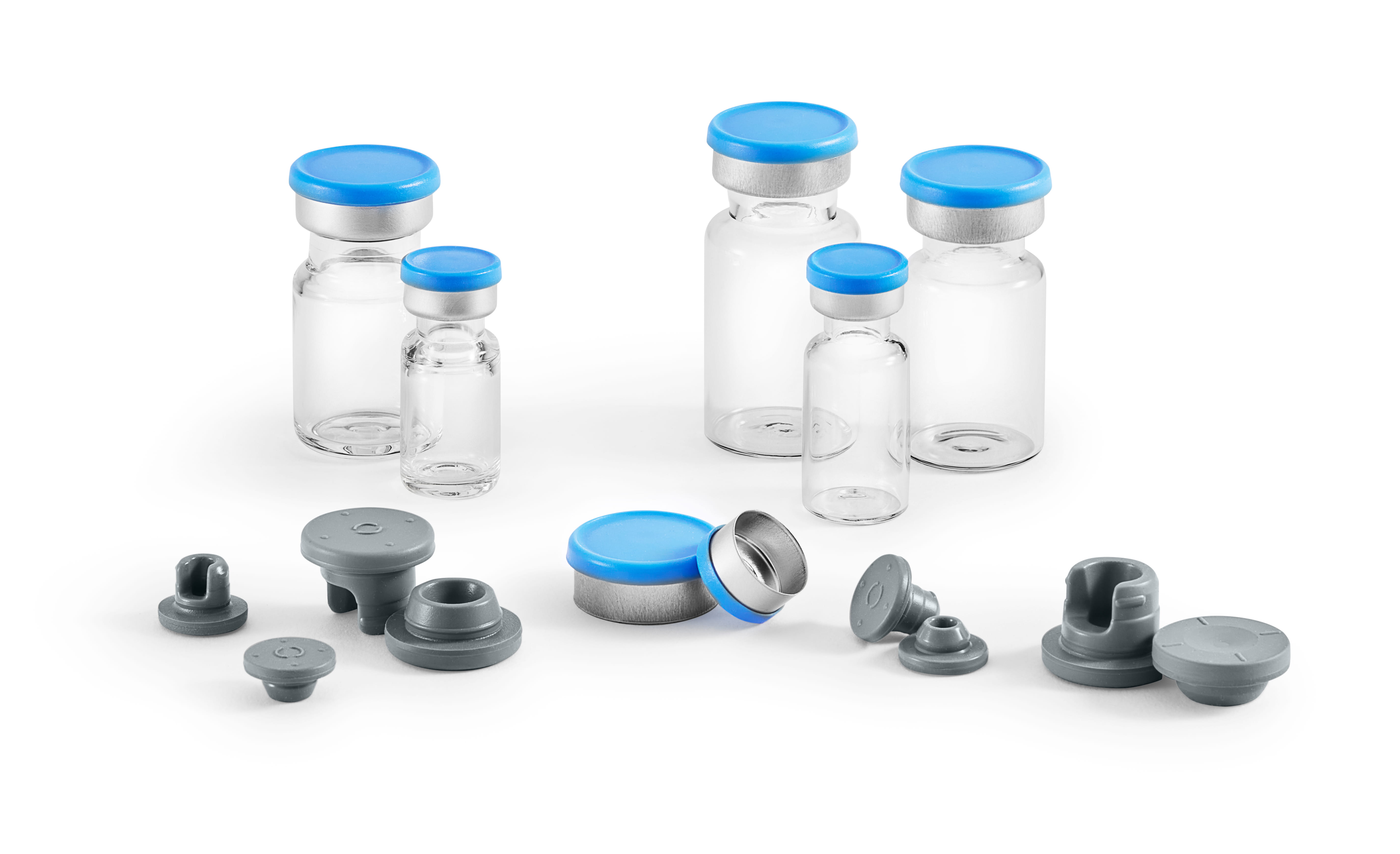

There are two types of tamper evident seals: all aluminum, where the tear-out or tear-off part that covers the stopper injection site is aluminum, which require two hands to open, and plastic-aluminum combination seals, which can be held and opened with one hand. The plastic cap on the latter seal is molded into the aluminum and the user can easily and safely remove the center aluminum ring by simply flipping off the plastic cap using the thumb while grasping the vial in their hand, as shown in Figure 1.
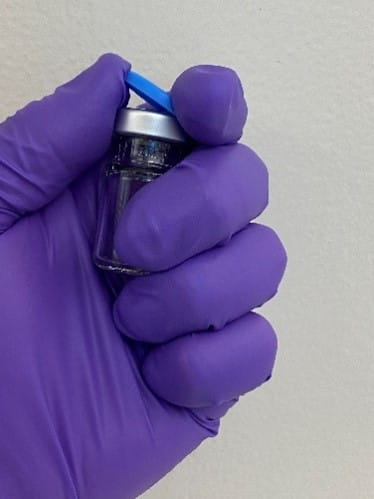
Figure 1 - One-handed vial cap flip-off.
The center aluminum part of the seal is typically attached to the rest of the ferrule by six (for 13 mm and 20 mm seals) thin aluminum bridges (Figure 2). Flipping off the plastic cap results in breaking of these bridges and exposing the stopper center to facilitate needle, spike, vial adaptor or other administration system penetration. Until the cap is removed, there is no way to access the stopper. Once the cap is removed and the bridges are broken, there is no way to re-attach the cap. As a result, this Flip-Off® seal cap serves as tamper evidence for the container-closure. West Pharmaceutical Services manufactures a number of different Flip-Off Seals to meet customer needs, which includes pre-sterilized seals, seals of different sizes to fit corresponding vials and bottles and with seal caps available in different colors. A technical overview of West’s Flip-Off Seals can be found here. These seals can be used for biologics, cell and gene therapy and in cryogenic applications. Additional discussions of seals for aseptic and clean crimping processes can be found here.

Figure 2 - Vial cap removed, showing broken bridges.
In order to ensure proper container-closure integrity, the appropriate vial, stopper and seal selection, coupled with optimal crimping conditions, must be developed. Component selection can be assisted by modeling the system using West’s DeltaCube®™ modeling platform or by choosing stopper-seal-vial combinations that were pre-selected to work together. Optimized crimping conditions can be developed by measuring the residual seal force of the crimped vial-stopper combination.
Once the vial-stopper-seal combination is optimized, it is important to establish that the Flip-Off Seal cap will stay on the vial until the user is ready to flip it off, as a number of conditions may potentially affect the force required to flip off the cap.ii Seal crimping conditions can cause the stopper to bulge in the center and exert forces on the seal that potentially could impact the integrity and breakage-resistance of the bridges. Likewise, cryogenic storage conditions that result in shrinkage of the metal seals can affect the strength of the bridges. In addition, simulated transportation conditioning (ASTM D4169-22iii) can affect the integrity of the bridges as the vial is jostled in its secondary container. While manufactured seals are factory tested to assure compliance with ISO and/or YBB flip-off force specifications as a matter of quality control, crimped and conditioned vials may need to be demonstrated to meet certain minimum flip-off force specifications to ensure that seal caps do not disengage during transportation and storage.
The aluminum-plastic combination seals and caps are covered by ISO 8362-6iv and ISO 8872v. The former Standard specifies that the force to remove the cap from a 13 mm seal must not exceed 25 Newtons while the force to remove the cap from a 20 mm seal must not exceed 35 Newtons. Meanwhile, the latter Standard provides a diagram of an apparatus to be used for measuring the required removal forces of the cap. These same upper limit specifications for cap removal force and similar test equipment are also proscribed in the Chinese Standard, YBB 00372003-2015.vi However, the Chinese Standard also specifies a minimum flip-off force of 6 N, for both the 13 mm and 20 mm seals, to ensure that the cap does not easily tear off accidentally. A test apparatus like that described in the Standards was custom-designed for West analytical services to measure the flip-off forces for crimped vials on a universal testing machine (Figure 3).
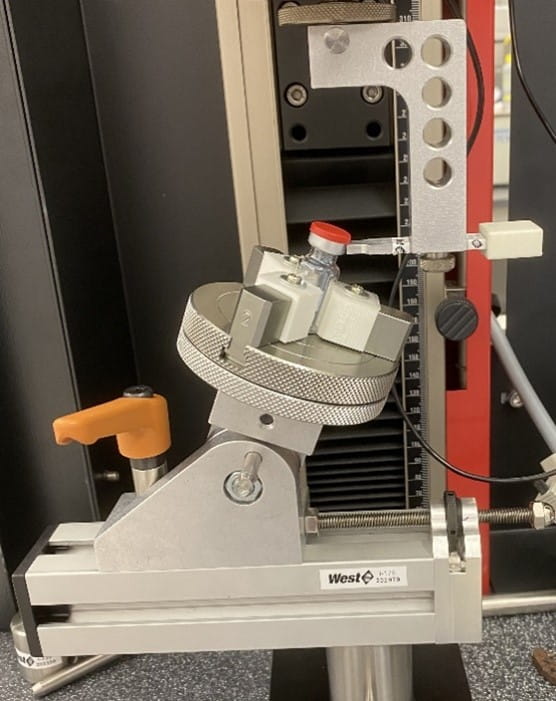

Figure 3 - Custom-designed apparatus for measuring Flip-Off Seal cap removal force.
West has validated a platform test method for measuring the cap removal force from crimped 13 mm and 20 mm Flip-Off Seal vials. Because the test is destructive (i.e., the sample is destroyed when the cap is pulled off such that the sample cannot be retested to establish repeatability) surrogate samples were developed that could be tested and retested for repeatability and reproducibility in a Gage R&R study.vii This validated method can be used in Design Verification Testing to examine customer vial samples to ensure that after commercial crimping and after simulated transportation conditioning or storage conditioning the cap is still securely attached to the seal and that the vial stopper is protected from tampering and contamination.
Contact West to learn more about West’s vial seals and how we can help you with your container-closure and combination product testing needs. For more information on West’s studies regarding Flip-Off Seals’ compatibility with West stoppers, along with other technical information, please visit the West Knowledge Center.
This article is for informational purposes only. West’s products and solutions are sold on the basis that it is the customer’s responsibility to evaluate and test the West product or solution to determine its compatibility with other materials and fitness for any end use. WEST MAKES NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, RELATING TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS ARTICLE.
Flip-Off® and DeltaCube® are registered trademark of West Pharmaceutical Services, Inc. in the United States and other jurisdictions.
References
iWhile the Flip-Off Seal is not a sterile barrier in itself, it serves to retail the stopper on the vial and the stopper is the sterile barrier. Without the seal, the stopper can dislodge or be removed from the vial and lead to potential contamination.
iiMathaes, R., et. al. (2016) The Pharmaceutical Capping Process—Correlation between Residual Seal Force, Torque Moment, and Flip-off Removal Force.
PDA Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 70 (3) 218-229. https://journal.pda.org/content/70/3/218.full
iiiASTM D4169-22
Standard Practice for Performance Testing of Shipping Containers and SystemsivISO 8362-6:2010
Injection containers and accessories – Part 6: Caps made of aluminium-plastics combinations for injection vialsvISO 8872:2022
Aluminium caps and aluminium/plastic caps for infusion bottles and injection vials – General requirements and test methodsviNational Standard of the People’s Republic of China. YBB 00372003-2015.
Aluminium-plastics Combination Caps for Antibiotics BottlesviiAutomotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) (2010). Measurement
Systems Analysis Reference Manual, 4th edition. Chrysler, Ford, General Motors Supplier Quality Requirements Task Force.






